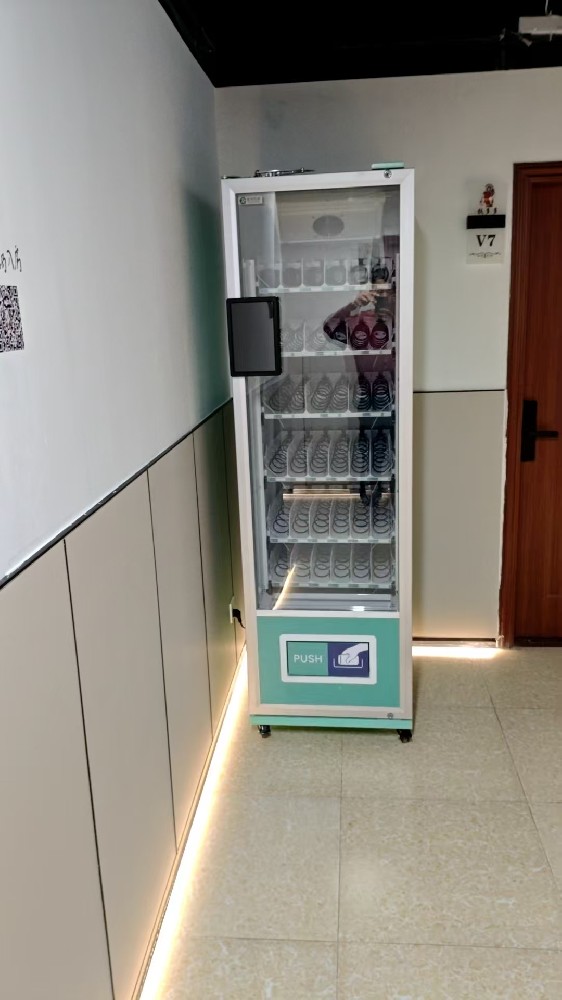
The rich aroma of freshly ground coffee has become an indispensable daily ritual in modern society, offering habitual comfort to billions worldwide. However, acquiring this essential daily brew has often involved queues, inconsistent quality, and the limitations inherent to human-operated, fixed-location service. The emergence of intelligent unattended coffee systems is fundamentally changing this landscape—these highly sophisticated automated terminals promise professional-grade coffee experiences anytime, anywhere. They are far more than mere beverage dispensers; they represent a deep convergence of robotics, the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence, and food process engineering, redefining how consumers access quality caffeine. This article provides an in-depth analysis of the technological core, market advantages, existing challenges, and future development of this innovative system.
The Technological Core: Evolution from Simple Dispensing to Precision Production
The era of simple push-button machines offering standardized drinks is over. Contemporary high-end unattended coffee systems are, in essence, highly integrated micro-factories:
Fully Automated Fresh-Grind Extraction Systems: The core lies in the complete "bean-to-cup" solution. The system features a built-in professional-grade grinder that mills fresh coffee beans on demand upon receiving an order, ensuring the complete preservation of aromatic compounds. It then precisely controls the dose and tamping pressure before extracting under constant temperature and pressure, fully replicating the core brewing logic of professional espresso machines. Most units also integrate fresh milk refrigeration and automatic frothing systems (or high-quality milk powder reconstitution solutions), multi-flavor syrup modules, and can be expanded to include tea and hot chocolate functions.
IoT and Cloud-Based Intelligent Management: Each device operates as an IoT node connected to a cloud management platform. This allows operators to remotely monitor all critical data in real-time: raw material inventory (coffee beans, milk, water, consumables), equipment operational status (sensor data, component health), real-time sales reports, and supports over-the-air firmware and software updates. An intelligent alert system proactively notifies maintenance personnel of low stock or machine anomalies, significantly optimizing operational efficiency.
Interactive Customization Interface: Equipped with high-definition large touchscreens, these systems provide intuitive graphical guidance. Users experience an ordering process akin to a professional café: selecting coffee bean origin and roast profile, adjusting coffee strength and volume, customizing milk type and temperature (e.g., hot, warm, or cold foam), adding various flavor syrups, and freely adjusting sweetness. Cup size selection is also standard.
Seamless Multi-Payment Integration: Comprehensive support for modern payment ecosystems, including cash acceptance modules, contactless bank/credit cards, mainstream mobile payments (e.g., Apple Pay, Alipay, WeChat Pay), and widely used QR code scanning. Some systems support deep integration with brand-owned apps for features like pre-ordering, online payment, and membership rewards.
AI-Powered Optimization: Cutting-edge systems are beginning to incorporate AI algorithms to enable predictive maintenance (forecasting potential failures by analyzing operational data), dynamic fine-tuning of brewing recipes based on environmental parameters (like ambient temperature and humidity), analysis of sales trends to intelligently suggest inventory management and menu updates, and, with user authorization, provide personalized beverage recommendations based on individual taste history.
Core Advantages: Key Drivers of Market Growth
The rapid proliferation of unattended coffee systems is fueled by the tangible value they deliver to all stakeholders in the supply chain:
Ultimate Convenience and Omni-Scenario Coverage: 24/7 uninterrupted service perfectly meets the needs of shift workers, transit hub travelers, university students, and anyone craving coffee outside traditional operating hours. Their flexible deployment capability allows them to penetrate locations traditionally difficult for cafés to cover, such as office buildings, hospitals, schools, gas stations, public squares, and industrial parks.
Significant Reduction in Operational Cost and Complexity: For operators, eliminating the need for professional baristas directly saves high labor costs and associated management burdens. Compared to opening a physical store, the equipment requires minimal space and no complex fit-out, drastically reducing initial investment and daily operational overhead. Cloud-based management makes multi-location, scaled operations simple and efficient.
Absolute Consistency in Product Quality: The fully automated process ensures every beverage is made with precise, unchanging parameters. Key variables like grind size, water temperature, extraction time, and milk foam density are meticulously controlled by the machine, completely eliminating human operational variability and achieving highly standardized, predictable flavor.
High Efficiency and Zero-Wait Experience: Eliminating queues, users can receive a customized fresh coffee in an average of 1-3 minutes, far more efficient than traditional cafés during peak hours. This is immensely attractive in time-sensitive locations like airports and business centers.
Enhanced Hygiene Standards and Reduced Contact: The automated, enclosed preparation process minimizes human contact points during production. Automatic dispensing of single-use cups, touchscreens with antimicrobial coatings, or optional contactless gesture controls significantly elevate hygiene and safety standards.
Data-Driven Precision Operations: The rich data accumulated in the system backend (including drink-specific sales, time distribution, ingredient consumption, etc.) provides operators with valuable insights for decision-making, enabling precise product mix optimization, dynamic pricing strategies, and scientific equipment placement planning.
Facing Challenges: Pending Issues on the Industry's Path Forward
Despite the promising prospects, the industry must confront and overcome the following obstacles:
Consumer Perception and Quality Trust: The primary task is to completely overturn the entrenched stereotype that "vended coffee equals low quality and cheap." This requires continuous market education, transparent display of ingredients, and consistently excellent product experiences to gradually build consumer trust in machine-produced, high-quality coffee.
High Initial Investment and Maintenance Threshold: The acquisition cost of these highly integrated, complex devices is significantly higher than that of traditional machines. Their maintenance and repair require personnel with specialized skills, and spare parts for core components are costly. While remote diagnostics can alleviate some pressure, they cannot fully replace on-site technical support.
Complexity of Supply Chain and Logistics Management: The use of short-shelf-life ingredients like fresh milk imposes higher demands on cold-chain storage and frequent restocking, increasing operational complexity and logistics costs compared to machines using longer-lasting, stable ingredients.
Relatively Singular Experience Dimension: These systems cannot replicate the social atmosphere, human touch, and interaction with professional baristas offered by traditional cafés. They primarily attract consumers whose core demands are efficiency, convenience, and consistent quality.
Fierce Competitive Landscape: They face competition not only from traditional cafés but also from convenience store fresh coffee offerings, emerging unattended retail formats, and the increasingly powerful on-demand delivery services.
Future Trends: Imagining the Next Cup
Looking ahead, unattended coffee systems will continue to evolve:
Deeper Ecosystem Integration: Achieving more profound data and service integration with mobile apps, social media, enterprise office systems, and smart city platforms.
Hyper-Personalized Experiences: AI will more precisely recommend exclusive beverages based on personal health data, real-time mood, or specific scenarios.
Green and Sustainable Development: Widespread adoption of biodegradable eco-friendly cups, energy recovery systems (e.g., utilizing waste heat), and more water-efficient cleaning technologies.
Expanded Product Matrix: Combining light meals, pastries, or retail goods, evolving towards a micro-unattended convenience store model.
Immersive Interactive Upgrades: Exploring the use of AR interfaces to enhance ordering fun or providing an artistic view of the coffee-making process through transparent viewing windows.
Conclusion
Unattended intelligent coffee systems have far surpassed the scope of automated beverage vending. They represent the forefront of the convergence of automation, digitalization, and networking in the foodservice industry, using technology to make high-quality coffee consumption ubiquitous and readily accessible. While continuously enhancing convenience, consistency, and accessibility, this innovative model is carving out a solid and growing niche in the global retail ecosystem. As technology advances and consumer habits deepen, these tireless "intelligent baristas" are destined to play an increasingly central role in the new map of global coffee demand, vividly illustrating how a perfect cup of coffee can stem from the exquisite fusion of technology and human-centric design.